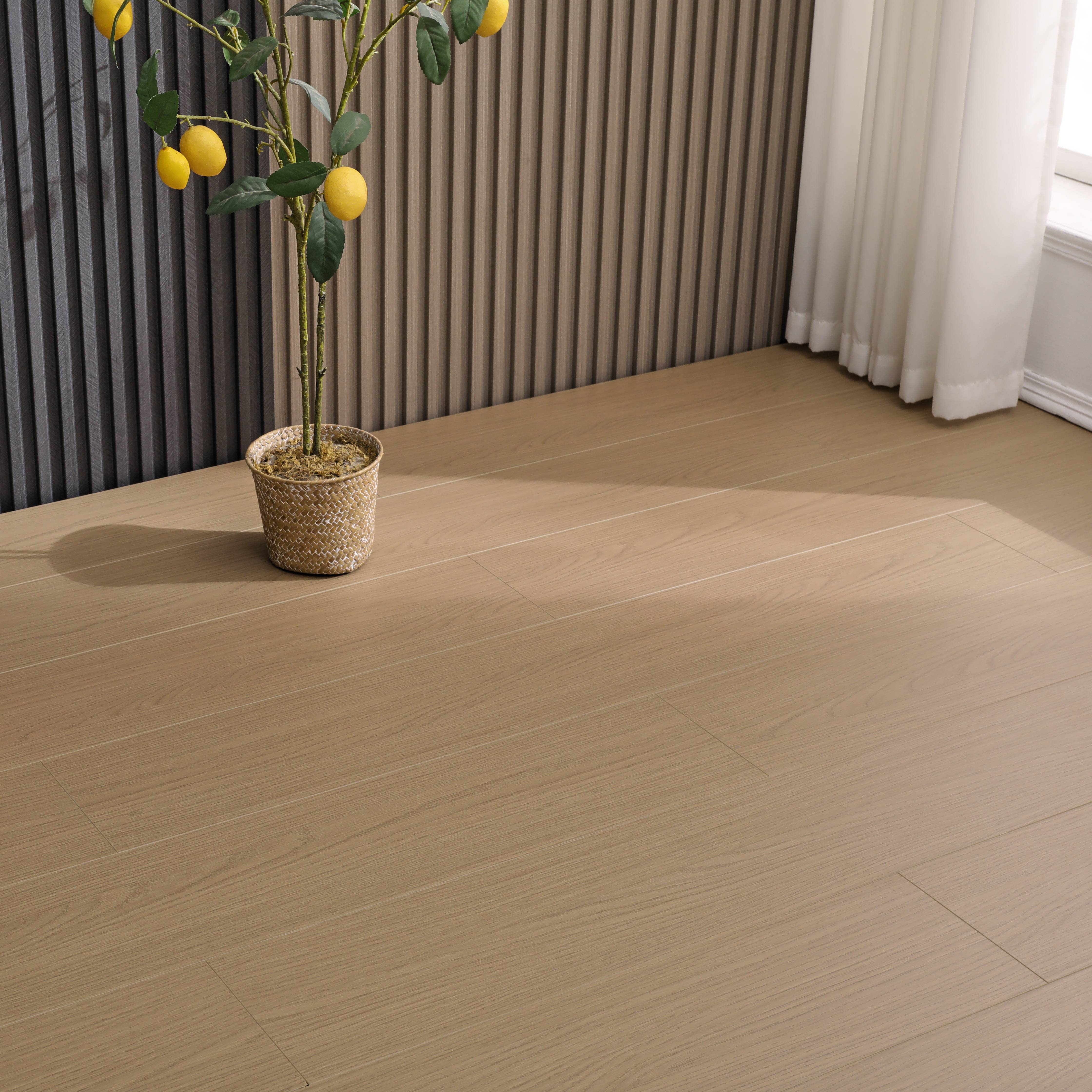
In today's competitive industrial landscape, ensuring the longevity and performance of packaging materials has become a critical concern for businesses across various sectors. The anti-slip packaging board stands out as an essential component in securing cargo during transportation and storage. These specialized boards provide the necessary friction and stability to prevent goods from shifting, sliding, or sustaining damage during handling processes. Understanding how to maximize their durability not only protects your investment but also ensures consistent performance over extended periods of use.

Understanding Anti-Slip Packaging Board Construction
Material Composition and Design Features
The foundation of any durable anti-slip packaging board lies in its material composition and manufacturing process. High-quality boards typically incorporate multi-layer construction with specialized surface treatments that enhance grip while maintaining structural integrity. The core material often consists of engineered wood fibers, composite materials, or high-density fiberboard that provides excellent strength-to-weight ratios. Surface coatings may include polymer-based treatments, textured films, or embedded particles that create the anti-slip properties essential for cargo security.
Modern manufacturing techniques ensure that these boards maintain consistent thickness and surface texture across their entire surface area. This uniformity is crucial for predictable performance and longevity. The bonding agents used in production must be resistant to moisture, temperature fluctuations, and chemical exposure to prevent delamination over time. Quality manufacturers often incorporate UV-resistant additives to prevent degradation when boards are exposed to sunlight during outdoor storage or transportation.
Performance Standards and Quality Indicators
Evaluating the quality of anti-slip packaging board requires understanding industry performance standards and testing protocols. Reputable manufacturers conduct comprehensive testing for friction coefficients, load-bearing capacity, moisture resistance, and dimensional stability. The friction coefficient, typically measured using standardized methods, determines the board's effectiveness in preventing cargo movement under various load conditions. Higher-quality boards maintain consistent friction values even after repeated use cycles.
Load-bearing specifications indicate the maximum weight the board can support without structural failure or permanent deformation. This capacity directly impacts durability, as boards operating within their designed limits experience less stress and maintain their properties longer. Moisture resistance testing reveals how well the board performs in humid environments or when exposed to liquid spills, which is particularly important for shipping applications where condensation or weather exposure may occur.
Installation and Initial Setup Best Practices
Proper Handling and Storage Procedures
The longevity of anti-slip packaging board begins with proper handling from the moment of delivery. These boards should be stored in clean, dry environments away from direct sunlight and extreme temperature variations. Stacking procedures must distribute weight evenly to prevent warping or surface damage. When moving boards, lifting techniques should minimize bending or flexing that could compromise structural integrity. Workers should use appropriate protective equipment to avoid surface scratches or punctures during installation.
Temperature and humidity control in storage areas significantly impact board condition before use. Rapid temperature changes can cause expansion and contraction cycles that weaken bonding agents and surface treatments. Maintaining consistent environmental conditions helps preserve the dimensional stability and surface characteristics that are essential for anti-slip performance. Proper inventory rotation ensures that older boards are used first, preventing long-term storage degradation.
Surface Preparation and Positioning Techniques
Effective installation of anti-slip packaging board requires thorough preparation of the contact surfaces where the boards will be placed. Clean, dry surfaces free from oils, debris, or chemical residues provide the best foundation for optimal board performance. Surface irregularities should be addressed before board placement to ensure full contact and prevent stress concentrations that could lead to premature failure. Proper positioning techniques distribute loads evenly across the board surface.
When positioning multiple boards, maintaining consistent spacing and alignment prevents cargo from settling into gaps where shifting could occur. Edge protection measures, such as beveled transitions or protective strips, help prevent damage from cargo loading equipment. The orientation of the anti-slip surface relative to expected load directions should align with manufacturer recommendations to maximize friction effectiveness and minimize wear patterns.
Maintenance Strategies for Extended Service Life
Regular Inspection and Assessment Protocols
Implementing systematic inspection routines is fundamental to maintaining anti-slip packaging board performance over time. Visual assessments should check for surface wear patterns, delamination signs, edge damage, or contamination that could affect friction properties. Tactile inspections help identify surface smoothing or texture loss that may not be immediately visible but could compromise anti-slip effectiveness. Documentation of inspection findings enables tracking of deterioration patterns and optimization of replacement schedules.
Measurement protocols should include thickness verification at multiple points to detect compression or wear. Surface roughness measurements using appropriate instruments can quantify texture degradation and determine when boards approach replacement thresholds. Load testing periodically verifies that boards maintain their structural capacity under expected operating conditions. These assessments help identify boards requiring removal before failure occurs during critical operations.
Cleaning and Surface Restoration Methods
Proper cleaning techniques significantly extend the service life of anti-slip packaging board by removing contaminants that could accelerate degradation. Cleaning solutions should be compatible with board materials and surface treatments to avoid chemical damage. Mechanical cleaning methods, such as brushing or scraping, must be gentle enough to preserve surface texture while effectively removing debris. High-pressure washing may be appropriate for certain board types but requires careful technique to prevent water infiltration into core materials.
Surface restoration techniques can rejuvenate worn anti-slip packaging board surfaces when replacement is not immediately necessary. Light sanding or abrading can restore texture to slightly worn surfaces, though care must be taken not to remove excessive material. Application of compatible surface treatments or coatings may restore anti-slip properties in some cases. However, these restoration methods require thorough testing to ensure they maintain or improve performance rather than creating unpredictable surface characteristics.
Environmental Protection and Weatherization
Moisture Management and Humidity Control
Effective moisture management represents one of the most critical factors in preserving anti-slip packaging board durability. Exposure to excessive humidity or direct water contact can cause swelling, warping, and degradation of bonding agents within the board structure. Implementing proper drainage systems and ventilation in storage and usage areas helps maintain optimal moisture levels. Vapor barriers or protective coatings may be necessary in high-humidity environments or applications with potential water exposure.
Monitoring relative humidity levels allows proactive adjustment of environmental conditions before damage occurs. Dehumidification systems or climate control equipment may be justified for high-value applications where board replacement costs are significant. When boards become wet, proper drying procedures prevent mold growth and minimize dimensional changes. Gradual drying at moderate temperatures typically produces better results than rapid high-temperature drying that could cause cracking or surface damage.
UV Protection and Chemical Resistance
Ultraviolet radiation exposure can significantly degrade anti-slip packaging board surfaces and bonding materials over time. UV-resistant coatings or additives incorporated during manufacturing provide some protection, but additional measures may be necessary for prolonged outdoor exposure. Protective covers, shade structures, or UV-filtering films can extend board life in applications where sun exposure is unavoidable. Regular rotation of board positions can distribute UV exposure more evenly across multiple units.
Chemical resistance becomes important when boards may contact oils, solvents, cleaning agents, or cargo residues. Understanding the chemical compatibility of board materials helps prevent degradation from specific substances encountered in particular applications. Prompt cleanup of chemical spills prevents prolonged contact that could cause permanent damage. In environments with regular chemical exposure, selecting boards specifically formulated for enhanced chemical resistance may be more cost-effective than frequent replacements of standard boards.
Load Distribution and Weight Management
Calculating Safe Load Limits
Proper load distribution across anti-slip packaging board surfaces is essential for preventing overload conditions that accelerate wear and potentially cause sudden failure. Understanding the relationship between point loads, distributed loads, and board capacity helps optimize cargo arrangement for maximum durability. Safety factors should account for dynamic loading conditions during transportation where acceleration, braking, and vibration create additional stresses beyond static weight considerations.
Load calculations must consider both the immediate weight of cargo and any concentration effects from small contact areas or sharp edges. Spreading loads across larger surface areas reduces local stress concentrations that could cause indentation or surface damage. When multiple boards are used together, load sharing between adjacent boards affects individual board stress levels and overall system durability. Proper edge support and interconnection methods help achieve more uniform load distribution.
Impact Prevention and Shock Absorption
Impact resistance plays a crucial role in anti-slip packaging board longevity, particularly in applications involving material handling equipment or rough transportation conditions. Understanding the impact energy absorption characteristics of different board constructions helps select appropriate materials for specific applications. Cushioning layers or protective mats can reduce impact forces transmitted to boards during loading operations or cargo shifting events.
Shock absorption techniques may include strategic placement of resilient materials between cargo and boards or incorporation of flexible mounting systems that reduce transmitted forces. Impact damage typically appears as surface indentations, cracks, or delamination that compromises both structural integrity and anti-slip performance. Preventive measures often prove more cost-effective than repairs or premature replacement of damaged boards.
Replacement Planning and Lifecycle Management
Performance Monitoring and Data Collection
Systematic performance monitoring enables data-driven decisions about anti-slip packaging board replacement timing and optimization of usage patterns. Tracking metrics such as surface wear rates, load cycles, environmental exposure, and maintenance requirements provides insight into actual service life under specific operating conditions. This data helps refine replacement schedules to balance safety requirements with cost optimization objectives.
Documentation systems should record board installation dates, usage patterns, inspection results, and any incidents or unusual conditions encountered during service. Correlation of performance data with environmental conditions, load characteristics, and maintenance practices identifies factors most significantly affecting durability. This information guides improvements in installation, maintenance, and operating procedures that can extend service life and reduce total ownership costs.
Upgrade Opportunities and Technology Improvements
Advances in materials technology and manufacturing processes continually improve the durability and performance characteristics of anti-slip packaging board products. Staying informed about new developments helps identify opportunities to upgrade to more durable solutions when replacement becomes necessary. Enhanced surface treatments, improved core materials, and better bonding technologies may offer significant improvements in service life and performance consistency.
Evaluation of upgrade options should consider both immediate performance improvements and long-term cost implications. Higher initial costs for premium materials may be justified by extended service life, reduced maintenance requirements, or improved safety performance. Pilot testing of new products under actual operating conditions provides valuable performance data before committing to large-scale replacements. Technology improvements may also enable expansion into new applications or operating conditions previously considered unsuitable for anti-slip packaging board solutions.
FAQ
How often should anti-slip packaging boards be inspected for wear and damage
The inspection frequency for anti-slip packaging board depends on usage intensity and operating conditions, but monthly visual inspections are recommended for most applications. High-traffic or heavy-load applications may require weekly inspections, while lighter-duty uses might extend to quarterly assessments. Critical applications such as hazardous material transport should implement more frequent inspection schedules. Always inspect boards immediately after any incident involving unusual impacts, spills, or environmental exposure that could affect performance.
What are the most common causes of premature failure in anti-slip packaging boards
Moisture exposure represents the leading cause of premature anti-slip packaging board failure, followed by overloading beyond design capacity and improper installation techniques. Chemical contamination from spills or cleaning agents can rapidly degrade surface treatments and bonding materials. Impact damage from dropped cargo or equipment contact creates stress concentrations that propagate into larger failures. Poor storage conditions, including temperature extremes and UV exposure, also contribute significantly to reduced service life.
Can damaged anti-slip packaging boards be repaired or must they be completely replaced
Minor surface damage such as light scratches or small indentations may be repairable through sanding and surface treatment renewal, but structural damage typically requires complete replacement. Delamination, cracking, or significant thickness loss cannot be reliably repaired and compromises both load-bearing capacity and anti-slip effectiveness. Edge damage may be repairable by trimming affected areas if sufficient material remains to meet application requirements. However, repairs should only be attempted when safety is not compromised and performance can be verified through appropriate testing.
What storage conditions maximize the shelf life of unused anti-slip packaging boards
Optimal storage conditions for anti-slip packaging board include temperature ranges between 60-80°F with relative humidity maintained between 30-50%. Storage areas should provide protection from direct sunlight and precipitation while allowing adequate air circulation to prevent moisture accumulation. Boards should be stored flat or properly supported to prevent warping and separated by protective materials to avoid surface scratching. Rotation of inventory ensures older boards are used first, and regular inspection of stored boards helps identify any degradation before use in critical applications.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Anti-Slip Packaging Board Construction
- Installation and Initial Setup Best Practices
- Maintenance Strategies for Extended Service Life
- Environmental Protection and Weatherization
- Load Distribution and Weight Management
- Replacement Planning and Lifecycle Management
-
FAQ
- How often should anti-slip packaging boards be inspected for wear and damage
- What are the most common causes of premature failure in anti-slip packaging boards
- Can damaged anti-slip packaging boards be repaired or must they be completely replaced
- What storage conditions maximize the shelf life of unused anti-slip packaging boards